How to Calculate GPA: Complete Guide to Understanding Your Grade Point Average
Calculating your Grade Point Average (GPA) is one of the most important academic skills you'll need throughout your educational journey. Whether you're a high school student preparing for college applications, an undergraduate aiming for graduate school, or simply tracking your academic progress, understanding how to calculate GPA accurately is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about GPA calculation, from basic formulas to advanced techniques for weighted grades.
What is GPA and Why Does It Matter?
GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a standardized numerical representation of your academic performance over a specific period. It converts letter grades into numerical values and calculates an average that reflects your overall academic achievement. Most institutions in the United States use a 4.0 scale, where an A equals 4.0, B equals 3.0, C equals 2.0, D equals 1.0, and F equals 0.0. Your GPA serves multiple crucial purposes: it determines your eligibility for academic honors, affects scholarship opportunities, influences college admissions decisions, and can even impact job prospects after graduation. Understanding how to calculate and interpret your GPA empowers you to set realistic academic goals and track your progress effectively.
Understanding the 4.0 GPA Scale
The 4.0 scale is the most widely used GPA system in American education. This scale assigns numerical values to letter grades, creating a standardized measure of academic achievement. An A grade receives 4.0 points, representing excellent performance and mastery of course material. A B grade earns 3.0 points, indicating above-average work. A C grade translates to 2.0 points for satisfactory performance, while a D grade receives 1.0 point for barely passing work. An F grade results in 0.0 points, indicating failure to meet course requirements.
Many schools also recognize plus and minus grades, which add nuance to the 4.0 scale. For example, an A- might be worth 3.7 points, a B+ could equal 3.3 points, and a B- might receive 2.7 points. However, note that grading scales can vary between institutions, so always confirm your school's specific conversion chart. Some schools don't award A+ grades (keeping the maximum at 4.0), while others assign A+ a value of 4.3 or maintain it at 4.0.
| Letter Grade | Percentage Range | GPA Points (4.0 Scale) | Quality Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | 93-100% | 4.0 | Excellent |
| A- | 90-92% | 3.7 | Excellent |
| B+ | 87-89% | 3.3 | Good |
| B | 83-86% | 3.0 | Good |
| B- | 80-82% | 2.7 | Good |
| C+ | 77-79% | 2.3 | Satisfactory |
| C | 73-76% | 2.0 | Satisfactory |
| C- | 70-72% | 1.7 | Satisfactory |
| D+ | 67-69% | 1.3 | Passing |
| D | 65-66% | 1.0 | Passing |
| F | Below 65% | 0.0 | Failing |
How to Calculate Unweighted GPA Step-by-Step
Calculating your unweighted GPA is straightforward once you understand the basic formula. Unweighted GPA treats all courses equally regardless of their difficulty level, making it the simpler calculation method. Here's the comprehensive step-by-step process to calculate your unweighted GPA accurately.
Step 1: Convert Letter Grades to Grade Points
Begin by listing all your courses and their corresponding letter grades. Using your school's conversion chart, transform each letter grade into its numerical equivalent on the 4.0 scale. For example, if you earned an A in English, that converts to 4.0 points. A B in Mathematics becomes 3.0 points, and so on. Make sure you're using your institution's specific conversion system, as slight variations exist between schools.
Step 2: Add All Grade Points Together
Once you've converted all letter grades to numbers, add up all the grade points. This sum represents your total grade points earned across all courses. If you took five classes and earned grades of A (4.0), A (4.0), B (3.0), B (3.0), and C (2.0), your total would be 16.0 grade points.
Step 3: Divide by Number of Courses
Take your total grade points and divide by the total number of courses you've taken. This calculation gives you your unweighted GPA. Using the formula:
In our example: 16.0 ÷ 5 = 3.2 GPA
Practical Example: Calculating Semester GPA
Scenario: Sarah completed five courses this semester with the following grades:
- English Literature: A (4.0)
- Biology: B+ (3.3)
- World History: A- (3.7)
- Algebra II: B (3.0)
- Physical Education: A (4.0)
Calculation:
Total Grade Points = 4.0 + 3.3 + 3.7 + 3.0 + 4.0 = 18.0
Number of Courses = 5
Result: Sarah's semester GPA is 3.6, which is excellent!
Calculating Weighted GPA for Advanced Courses
Weighted GPA systems recognize that not all courses are equally challenging. Advanced Placement (AP), International Baccalaureate (IB), honors, and dual-enrollment courses require more rigorous work and deeper understanding. To acknowledge this additional difficulty, many high schools use a weighted GPA scale that awards extra points for advanced coursework. This system typically uses a 5.0 scale for AP and honors classes instead of the standard 4.0 scale.
In a weighted system, an A in an AP course receives 5.0 points instead of 4.0, a B earns 4.0 points instead of 3.0, and so on. Regular-level courses still use the standard 4.0 scale. This means your weighted GPA can exceed 4.0 if you take challenging courses and perform well. For detailed weighted GPA calculations, use our Weighted GPA Calculator or 5.0 GPA Calculator.
Weighted GPA Calculation Formula
Weighted GPA Example
Scenario: Michael took six courses including two AP classes:
- AP Calculus: A (5.0 on weighted scale)
- AP English: B+ (4.3 on weighted scale)
- Regular Chemistry: A (4.0)
- Regular Spanish: B (3.0)
- Regular History: A- (3.7)
- Regular Art: A (4.0)
Calculation:
Total Weighted Grade Points = 5.0 + 4.3 + 4.0 + 3.0 + 3.7 + 4.0 = 24.0
Number of Courses = 6
Result: Michael's weighted GPA is 4.0, while his unweighted GPA would be lower.
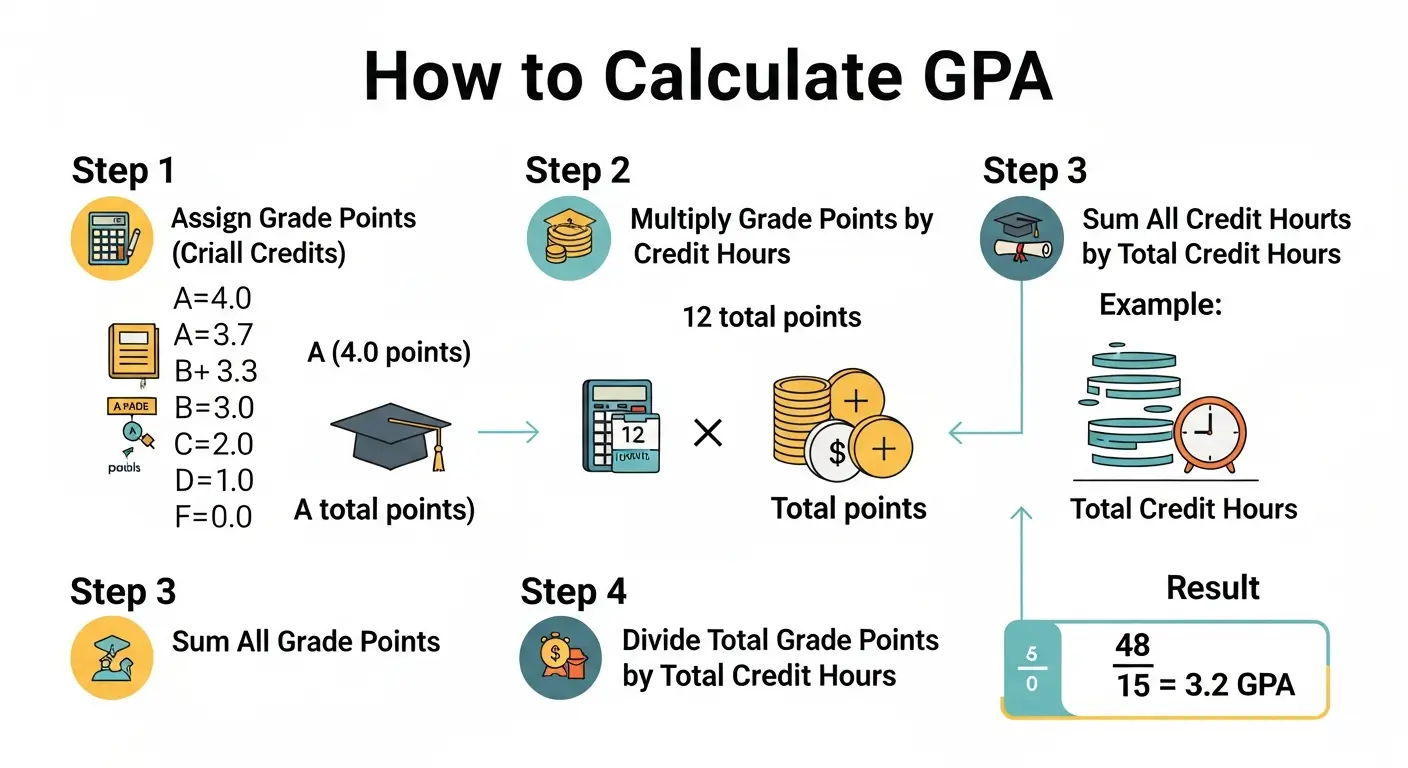
Calculating GPA with Credit Hours
College courses aren't all created equal in terms of time commitment and academic weight. A comprehensive laboratory science course might be worth 4 credit hours, while a seminar course might only carry 2 credits. Credit hours represent the amount of time you spend in class each week and reflect the course's weight in your overall GPA calculation. To calculate your GPA with credit hours accurately, you need to weight each grade by its credit value.
Credit-Weighted GPA Formula
This formula ensures that courses with more credit hours have a proportionally larger impact on your overall GPA. A poor grade in a 4-credit course will affect your GPA more than the same grade in a 1-credit course, which accurately reflects the greater time and effort invested.
Credit-Weighted GPA Example
Scenario: Jessica completed four courses with varying credit hours:
| Course | Grade | Grade Points | Credit Hours | Weighted Points |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Biology | A | 4.0 | 4 | 16.0 |
| English | B+ | 3.3 | 3 | 9.9 |
| Mathematics | A- | 3.7 | 3 | 11.1 |
| Physical Education | A | 4.0 | 1 | 4.0 |
Calculation:
Total Weighted Points = 16.0 + 9.9 + 11.1 + 4.0 = 41.0
Total Credit Hours = 4 + 3 + 3 + 1 = 11
Result: Jessica's credit-weighted GPA is 3.73
For college-level GPA calculations, check out our specialized College GPA Calculator and Undergraduate GPA Calculator.
Understanding Cumulative GPA vs Semester GPA
Students often confuse semester GPA with cumulative GPA, but understanding the distinction is crucial for tracking academic progress. Your semester GPA represents your grade point average for a single term only – typically one semester or quarter. It shows how well you performed during that specific period and resets each term. In contrast, your cumulative GPA is the average of all your semester GPAs combined, encompassing your entire academic history at an institution.
Your semester GPA can fluctuate significantly from term to term based on course difficulty, personal circumstances, and effort level. However, your cumulative GPA changes more gradually because it incorporates all previous academic work. This means a strong semester can boost your cumulative GPA, but it won't change dramatically overnight. Similarly, one poor semester won't destroy your cumulative GPA if you've maintained strong grades previously, though it will have an impact.
Calculating Cumulative GPA
To calculate your cumulative GPA, you multiply each semester's GPA by its credit hours, add all those products together, then divide by the total number of credit hours attempted across all semesters. Use our Cumulative GPA Calculator for quick and accurate cumulative calculations.
Cumulative GPA Calculation Example
Scenario: David has completed three semesters:
- Semester 1: 3.5 GPA with 15 credit hours = 52.5 grade points
- Semester 2: 3.8 GPA with 16 credit hours = 60.8 grade points
- Semester 3: 3.3 GPA with 14 credit hours = 46.2 grade points
Calculation:
Total Grade Points = 52.5 + 60.8 + 46.2 = 159.5
Total Credit Hours = 15 + 16 + 14 = 45
Result: David's cumulative GPA is 3.54
For semester-specific calculations, visit our Semester GPA Calculator, Quarter GPA Calculator, or Trimester GPA Calculator.
How to Calculate CGPA (Cumulative Grade Point Average)
CGPA, or Cumulative Grade Point Average, is commonly used in educational systems outside the United States, particularly in India, Pakistan, and parts of Europe. While similar in concept to GPA, CGPA typically uses a 10-point scale rather than a 4-point scale. Understanding how to calculate and convert CGPA is essential for students planning to study abroad or applying to international universities.
CGPA calculation involves grade points and credit hours similar to GPA, but the scale and methodology differ slightly. Each course receives a grade point based on your performance (typically ranging from 0 to 10), and these grade points are multiplied by the course's credit hours. The sum of all weighted grade points is then divided by the total credit hours to arrive at your CGPA.
CGPA Calculation Formula
CGPA Calculation Example
Scenario: Priya completed five subjects with the following grades and credits:
| Subject | Grade Points | Credits | Weighted Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mathematics | 9 | 4 | 36 |
| Physics | 8 | 4 | 32 |
| Chemistry | 8 | 3 | 24 |
| English | 7 | 3 | 21 |
| Computer Science | 9 | 3 | 27 |
Calculation:
Total Weighted Points = 36 + 32 + 24 + 21 + 27 = 140
Total Credits = 4 + 4 + 3 + 3 + 3 = 17
Result: Priya's CGPA is 8.24 out of 10
Converting CGPA to GPA (4.0 Scale)
For international applications, you may need to convert your CGPA to the 4.0 GPA scale. The most commonly used conversion formula is:
For example, if your CGPA is 8.5 out of 10, your GPA conversion would be: (8.5 ÷ 10) × 4.0 = 3.4 GPA. However, always verify conversion requirements with your target institution, as some universities use different conversion methods. Our Foreign GPA Calculator and International GPA Calculator can help with these conversions.
Converting Percentage to GPA
Many international education systems use percentage grading rather than letter grades or grade points. If you need to convert percentage grades to GPA for college applications or transfer purposes, several methods exist. The most straightforward conversion formula for percentage to GPA on a 4.0 scale is:
For example, if you scored 85% overall, your GPA would be: (85 ÷ 100) × 4.0 = 3.4 GPA. However, this linear conversion method may not always align with institutional requirements. Some schools use conversion tables that match percentage ranges to specific GPA values, similar to how letter grades convert to grade points. Always confirm the preferred conversion method with the institution where you're applying.
Use our specialized Percentage to GPA Calculator for accurate conversions between percentage grades and the 4.0 GPA scale.
Specialized GPA Calculations for Different Academic Levels
High School GPA
High school GPA calculations typically include all core academic courses plus electives. Some high schools include non-academic courses like physical education and arts in GPA calculations, while others exclude them. Weighted GPAs are particularly common at the high school level to differentiate students taking rigorous coursework. Colleges often recalculate high school GPAs using their own formulas, sometimes excluding non-core courses and standardizing weighting systems. Calculate your high school performance using our High School GPA Calculator.
Transfer GPA
When transferring between institutions, your GPA calculation can become complex. Transfer GPA typically includes only courses that transfer to your new institution and count toward your degree. Some schools calculate a separate transfer GPA that doesn't include grades from your previous institution in your new cumulative GPA, though the courses count for credit. Other schools incorporate all previous coursework into your cumulative GPA. Understanding transfer GPA policies is crucial for academic planning. Use our Transfer GPA Calculator to estimate how your grades will transfer.
Graduate and Professional School GPAs
Graduate programs often calculate GPA differently than undergraduate institutions. Many graduate schools require a minimum GPA for degree completion, typically 3.0 or higher, and courses below a B grade may not count toward your degree. Professional schools like law, medical, and business schools have specific GPA calculation methods and minimum requirements. Our specialized calculators can help: Law School GPA Calculator, Medical School GPA Calculator, MBA GPA Calculator, Graduate School GPA Calculator, and Engineering GPA Calculator.
Planning and Predicting Future GPA
Strategic GPA planning helps you set realistic academic goals and understand what grades you need to achieve target GPAs. Whether you're trying to raise your GPA for scholarships, maintain academic standing, or qualify for graduate programs, calculating required future grades is essential.
Calculating Required GPA
To determine what GPA you need in future semesters to reach a target cumulative GPA, use this formula:
For example, if you have a 3.2 cumulative GPA with 60 credits completed and want to achieve a 3.5 cumulative GPA after completing 90 total credits, you would need: [(3.5 × 90) - (3.2 × 60)] ÷ 30 = 4.1 GPA in your remaining 30 credits. This reveals whether your goal is achievable with excellent grades or if you need to adjust your target.
Use our planning tools to visualize your academic future: Required GPA Calculator, Target GPA Calculator, GPA Booster Calculator, GPA Predictor Calculator, What-If GPA Calculator, and Final GPA Calculator.
Understanding Grade Points
Grade points form the foundation of GPA calculations, yet many students don't fully understand them. Grade points are the numerical values assigned to letter grades that enable mathematical averaging of performance across courses. The grade point system standardizes diverse grading methods into a common scale, allowing fair comparison of academic achievement.
Each grade corresponds to a specific grade point value: A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, D = 1.0, F = 0.0. These values represent quality points that reflect performance level. When multiplied by credit hours, grade points become weighted values that account for course importance in your overall academic record. Our Grade Points Calculator can help you understand the relationship between grades and points.
Common Mistakes When Calculating GPA
Even with straightforward formulas, students frequently make errors when calculating their GPA. Being aware of these common pitfalls helps ensure accuracy and prevents disappointment when official transcripts arrive.
Mistake 1: Forgetting to Weight by Credit Hours
Many students simply average their grade points without considering that different courses carry different credit weights. A 4-credit biology course should impact your GPA more than a 1-credit seminar. Always multiply grade points by credit hours before adding them together, then divide by total credits.
Mistake 2: Using the Wrong Grading Scale
Not all schools use identical grade point values. Some institutions assign different point values to plus and minus grades, while others don't recognize them at all. Always verify your school's specific grading scale before calculating. An A- might be 3.7 at one school and 4.0 at another.
Mistake 3: Including or Excluding the Wrong Courses
Some GPA calculations include all courses, while others exclude pass/fail classes, withdrawn courses, or non-academic electives. Understand which courses count for your particular GPA type (term GPA, cumulative GPA, major GPA). Repeated courses present special challenges – some schools replace the old grade entirely, others average both attempts, and some include both separately.
Mistake 4: Rounding Too Early
Rounding intermediate calculations can introduce significant errors. Maintain at least two decimal places throughout your calculations and only round your final GPA result. Some students also round incorrectly – know whether your institution rounds to the nearest tenth or hundredth.
Mistake 5: Confusing Weighted and Unweighted GPA
Students often calculate weighted GPA when an unweighted GPA is required, or vice versa. College applications frequently ask for both, and mixing them up can misrepresent your academic record. Understand which type each application requires and calculate accordingly.
Mistake 6: Arithmetic Errors
Simple addition, multiplication, or division mistakes are surprisingly common, especially when calculating by hand. Double-check your arithmetic or use a calculator to verify results. Online GPA calculators can eliminate mathematical errors entirely.
Tips for Improving Your GPA
Understanding GPA calculation is just the first step – improving your GPA requires strategic planning and consistent effort. While you can't change past grades, you can maximize future performance to raise your cumulative GPA over time. Focus on courses with higher credit hours, as they provide more opportunity to positively impact your GPA. Prioritize classes in your major or areas of strength where you're more likely to earn high grades.
Consider retaking courses where you earned low grades if your institution's grade replacement policy allows it. Many schools will replace the old grade with the new one in GPA calculations, though both may remain on your transcript. Attend office hours, form study groups, and utilize tutoring resources to strengthen understanding in challenging subjects. Time management and consistent study habits prevent last-minute cramming and typically result in better grades.
Don't overload yourself with too many difficult courses in one semester. Balance challenging classes with courses where you can excel to maintain a strong semester GPA. Finally, understand that GPA improvement is gradual – one excellent semester won't dramatically change a cumulative GPA accumulated over years, but consistent strong performance will steadily raise it.
How Current GPA Affects Future Opportunities
Your GPA influences numerous aspects of your academic and professional future. Most scholarship programs establish minimum GPA requirements, with competitive scholarships often requiring 3.5 or higher. Graduate and professional schools use GPA as a primary screening criterion, with many programs setting minimum thresholds of 3.0 to 3.5 for admission consideration. Highly selective programs may require GPAs of 3.7 or higher.
Academic honors and distinctions like dean's list, cum laude, magna cum laude, and summa cum laude are GPA-based. These recognitions on your transcript and resume signal academic excellence to employers and admissions committees. Some employers, particularly competitive firms in finance, consulting, and technology, screen candidates based on GPA and may require minimums of 3.0 or 3.5 to even apply.
Academic standing also depends on GPA – falling below a certain threshold (typically 2.0) may result in academic probation or suspension. Understanding your GPA helps you monitor academic standing and take corrective action if needed. Finally, GPA affects eligibility for academic programs, research opportunities, internships, and teaching assistantships, many of which have GPA prerequisites.
Frequently Asked Questions About GPA Calculation
Specialized GPA Calculators
Explore our comprehensive collection of GPA calculators designed for every academic scenario:
Conclusion
Mastering GPA calculation empowers you to take control of your academic journey. Whether you're calculating a simple semester GPA, navigating complex weighted systems, or planning future coursework to achieve target cumulative GPAs, understanding the formulas and principles behind GPA gives you the tools to make informed educational decisions. Remember that while GPA is important for scholarships, admissions, and opportunities, it's only one measure of your capabilities and potential. Use it as a motivational tool and planning resource, but don't let it define your entire academic experience. With the knowledge from this guide and the specialized calculators available, you can accurately track your academic performance, set realistic goals, and work strategically toward your educational objectives.
GPA Questions & Answers: Everything You Need to Know
Complete answers to 100+ common questions about calculating, checking, and improving your GPA
Improving Your GPA
Learn strategies and techniques to raise your grade point average
Understanding GPA Basics
Fundamental concepts about what GPA is and how it's assigned
How to Check Your GPA
Methods to access and verify your current grade point average
Calculating Your GPA
Step-by-step guidance on computing your grade point average
Finding Your GPA
Locating where your GPA is displayed and recorded
Various GPA Calculation Methods
Different approaches to determining your grade point average
Cumulative GPA Calculations
Understanding how cumulative and overall GPA is computed
UCAS Points & UK Grading System
Understanding the UK's UCAS tariff point system
ATAR Calculation (Australian System)
Understanding Australia's ATAR ranking system